Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 4 - Practice Test No.1 (25 Ban)
Uploaded by
nguyen nga0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
284 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Unit 4 - Practice test No.1 (25 ban)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
284 views3 pagesUnit 4 - Practice Test No.1 (25 Ban)
Uploaded by
nguyen ngaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
English 11
Unit 4. CARING FOR THOSE IN NEED – PRACTICE TEST No. 1
PART 1: VOCABULARY AND GRAMMAR REVIEW
A. VOCABULARY
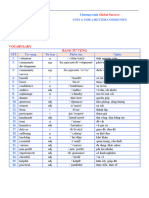
1.barrier /ˈbæriə(r)/ (n.) rào cản, chướng ngại vật
2.blind /blaɪnd/ (adj.) mù, không nhìn thấy được
3.campaign /kæmˈpeɪn/ (n.) chiến dịch
4.charity /ˈtʃærəti/ (n.) hội từ thiện, việc từ thiện
5.cognitive /ˈkɒɡnətɪv/ (adj.) liên quan đến nhận thức
6.deaf /def/ (adj.) điếc, không nghe thấy được
7.disability /ˌdɪsəˈbɪləti/ (n.) sự ốm yếu, tàn tật
disabled /dɪsˈeɪbld/ (adj.) (n.) người tàn tật
8.disrespectful /ˌdɪsrɪˈspektfl/ (adj.) thiếu tôn trọng
9.donate /dəʊˈneɪt/ (v.) quyên góp, tặng
10.dumb /dʌm/ (adj.) câm, không nói được
11.effectively /ɪˈfektɪvli/ (adv.) hiệu quả
12.impairment /ɪmˈpeəmənt/ (n.) sự suy yếu, hư hại, hư hỏng
13.integrate /ˈɪntɪɡreɪt/ (v.) hòa nhập, hội nhập
14.launch /lɔ:ntʃ/ (v.) phát động, khởi động
15.physical /ˈfɪzɪkl/ (adj.) (thuộc về) cơ thể, thể chất
16.principal /ˈprɪnsəpl/ (n.) hiệu trưởng
17.talent /ˈtælənt/ (n.) tài năng, người có tài
18.visual /ˈvɪʒuəl/ (adj.) (thuộc về) thị giác, có liên quan đến thị giác
19.volunteer /ˌvɒlənˈtɪə(r)/ (n.) người tình nguyện, tình nguyện viên
20.accessible /əkˈsesəbl/ (adj.) có thể tiếp cận được
21.coordination /kəʊˌɔːdɪˈneɪʃn/ (n.) sự hợp tác
22.discrimination /dɪˌskrɪmɪˈneɪʃn/ (n.) sự phân biệt đối xử
23.fracture /ˈfræktʃə(r)/ (n.) (v.) (chỗ/sự) gãy xương)
24.hardship /ˈhɑ:dʃɪp/ (n) sự vất vả
25.ingredient /ɪn'gri:diənt/ (n.) thành phần, nguyên liệu
26.involve /ɪnˈvɒlv/ (v.) bao gồm, bao hàm
27.limitation /ˌlɪmɪ'teɪʃn/ (n.) sự giới hạn, hạn chế
28.millennium /mɪ'leniəm/ (n.) thiên niên kỷ
29.mobility /məʊˈbɪləti/ (n.) tính di động, lưu động
30.pedestrian /pə'destriən/ (n.) người đi bộ
31.promote /prə'məʊt/ (v.) khuyến khích, đẩy mạnh, làm tăng thêm
32.rewarding /rɪ'wɔ:dɪŋ/ (adj.) bổ ích, đáng làm
33.support /səˈpɔːt/ (n.) (v.) (sự) ủng hộ, khuyến khích
34.vocational training /vəʊ'keɪʃənl 'treɪnɪŋ/ (n. phr.) đào tạo nghề
35.wheelchair /ˈwiːltʃeə(r)/ (n.) xe lăn .
PART 2: EXERCISES
A. PHONETICS
I. Choose the word whose underlined part is pronounced differently from that of the others in each
group.
1. A. comfort B. hobby C. knowledge D. popular
2. A. about B. announce C. cough D. shout
3. A. hood B. hook C. stood D. tool
4. A. done B. gone C. mum D. won
5. A. coup B. group C. soup D. tough
6. A. filled B. landed C. suited D. wicked
7. A. cloth B. clothe C. with D. without
8. A. cease B. chase C. increase D. raise
9. A. beds B. doors C. students D. plays
10. A. gypsy B. huge C. piggy D. strange
II. Pick out the words whose main stressed syllable is different from the rest.
1. A. silent B. children C. village D. advice
2. A. important B. performance C. silently D. permission
3. A. efficient B. flowery C. flourishing D. gramophone
4. A. inhabitant B. initiate C. engineering D. ingenious
5. A. content B. advice C. promise D. admire
III. Choose the suitable word to complete the sentence.
High School for Gifted Students - HNUE Page 1
English 11
1. Last week we interviewed some volunteers who had worked with disabled/disabilities students.
2. There are more devices to enable people with impairments/physical disabilities to travel around.
3. These are students with various visual, hearing/deaf, physical and cognitive impairments.
4. We need to help disabled students to become independent and integrate/launch in the community.
5. The students in our class have charity/donated more than 50 gifts.
IV. Complete the sentences using the given words.
impairments voluntary visual volunteers support
1. People with physical ________________________________ have difficulty climbing stairs.
2. This special school helps students with _________________________ impairments to learn Braille.
3. Many _________________________ have taken part in our programmes since the campaign was
launched.
4. We have launched various services to __________________________ people with learning disabilities.
5. We completed a ________________________ project for our community center a month ago.
V. Fill in each gap with the past simple or the present perfect form of the given word(s).
1. Last night I (lose) __________________________ my keys. I had to call my flatmate to let me in.
2. I (lose) __________________________ my keys. Can you help me look for them?
3. He (live) _____________________ with his great grandmother for a few years - she died when he was
eight.
4. She and her best friends (know) ___________________________ each other for over fifteen years. They
still get together once a week.
5. A: What's wrong?
B: I (break) __________________________ a glass.
6. She (be) __________________________ a teacher for ten years, and she still enjoys it.
7. How many times (she/ go) __________________________ to the cinema last month?
8. Aunt to Jonny: Jonny, I can't believe how much you've changed since the last time I saw you. You (grow)
__________________________ at least a foot!
9. A: How long (you/ live) __________________________ in Paris?
B: Twenty years. We came back to live in England in 2010.
10. A: How long (you/ live) __________________________ in Japan?
B: Four years. And we really like it here.
VI. Choose the suitable word to complete each sentence.
1. Last year I volunteered to teach at a school for people with hearing impairments and launched/have
launched a campaign to help them.
2. A: How many times did you try/have you tried to pass your driving test?
B: Three times so far.
3. A: I can't send my e-mails because my computer's broken.
B: How long was your computer/has your computer been broken?
A: About a week. I'm going to take it back to the shop when I have time.
4. A: I went to Japan on holiday last year.
B: How long were you/have you been there?
A: Only two weeks. It wasn't really long enough to see everything.
5. A: When did he arrive/has he arrived?
B: He arrived at 2 o'clock.
6. A: Why don't you want to play football with us this weekend?
B: I broke/have broken my leg.
7. A: I never drank/have never drunk whiskey.
B: Have some now.
8. My best friend, Linh went to Canana two years ago, but I wasn't/haven't been there so far.
C. READING
I. Read the passage and answer the following questions.
Each summer, the Winant and Clayton Volunteer program sends a group of Americans to volunteer
in London for seven weeks and provides housing and a small stipend to help defray the high cost of living.
After seven weeks of volunteering, participants have two weeks to travel independently before returning to
London to evaluate the program and get their flight back to the United States.
The application includes a few short essays, a series of questions about the type of placement one
would prefer, and an informal interview with former volunteers that gives applicants a chance to find out
more about the program.
Deciding to participate takes a small leap of faith. The roster of volunteer placements and housing
options can change from year to year and volunteers can't choose their placement in advance. But once
you're accepted you instantly feel that you've joined a close-knit group. The volunteer coordinator is in
High School for Gifted Students - HNUE Page 2
English 11
frequent contact through mailings and e-mails to help you prepare for the trip, and there is a daylong
orientation in New York that bring all the volunteers together before departure for London.
1. How long do a group of Americans volunteer in London?
A. two weeks B. each summer C. seven weeks D. three weeks
2. What does the Winant and Clayton Volunteer program provide them with?
A. housing and a small stipend B. a few short essays
C. transportation D. foods and clothes
3. Which of the following is NOT included in the application?
A. A series of questions about the type of placement one would prefer
B. An informal interview with former volunteers
C. A few short essays
D. The roster of volunteer placements
4. What can the volunteers do after seven weeks of volunteering?
A. They can have two weeks to travel independently
B. They can have two weeks to evaluate the program
C. They can return to London
D. They can get their flight back to the United States
5. How does the volunteer coordinator keep in contact with you?
A. Through television and newspapers B. Through telephone and e-mails
C. Through mailings and e-mails D. Through radio and cell phone
II. Read the following passage and choose the best option.
The United States has been criticized for its treatment of its elderly citizens. Although in many other
countries the elderly usually live with their children's family, many older Americans live alone, without the
close companionship of their children. This situation is sometimes blamed on the "selfishness" of the young
generation, but a closer look shows that many of the elderly prefer to maintain their independent lives.
Research on the situation of the elderly in America has shown that while grandparents are delighted to be
visited periodically by their children and grandchildren, they prefer to continue living in the surroundings
that they are familiar with. This suggests that children should permit their parents to live alone if they wish
to, and should encourage them to maintain close ties to the rest of the family.
Another surprising result of the research on the elderly in the United States has been the very
positive influence which pets have been found to have on the elderly people that they live with. It has been
shown that elderly people who care for small pets, such as cats and dogs, live longer, are healthier, and have
better attitudes towards their lives than similar elderly people without these companions.
1. Many elderly Americans live ____.
A. without satisfaction. B. by themselves.
C. a lonely life. D. a simple life.
2. What do some people see as the cause of this situation?
A. The society of the USA treats its elderly people as troubles.
B. The young people usually trouble the elderly of their own.
C. The government concerns hardly about the elderly people.
D. The young people are too selfish.
3. Many of the elderly Americans want to ____.
A. keep living in their well-known places and conditions.
B. remain with the grandchildren in their houses.
C. remove to their sons' or daughters' homes.
D. live with their friends in their hometown.
4. The author advises the young people to ____.
A. keep close ties with the elderly of their own.
B. let the elderly of their families live by themselves.
C. permit their elderly relatives to raise some pets.
D. respect the wishes of their elderly parents.
5. The author's main thought is that ____.
A. the elderly who care for some pets live together.
B. the social practice in the USA makes the elderly live alone.
C. the elderly people should have better attitudes towards their lives.
D. it is a social tradition that the elderly Americans enjoy the self-directing lives.
High School for Gifted Students - HNUE Page 3
You might also like
- 21 Cách Học Tiếng Anh Du Kích: Tiếng Anh Du Kích, #1From Everand21 Cách Học Tiếng Anh Du Kích: Tiếng Anh Du Kích, #1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bài Tập Tiếng Anh Lớp 8 Bùi Văn VinhDocument206 pagesBài Tập Tiếng Anh Lớp 8 Bùi Văn VinhThaoly PhanhoangNo ratings yet
- De Cuong 12 - 492021184447Document105 pagesDe Cuong 12 - 492021184447AN NGUYEN NGOC BAONo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Tiếng Anh Lớp 8 Bùi Văn VinhDocument186 pagesBài Tập Tiếng Anh Lớp 8 Bùi Văn VinhBùi Thảo ChiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Local Environment (10 Ban)Document5 pagesUnit 1 - Local Environment (10 Ban)nguyen nga100% (1)
- Bài-tập-Tiếng-Anh-8-Bùi-Văn-Vinh- (bản đẹp) PDFDocument186 pagesBài-tập-Tiếng-Anh-8-Bùi-Văn-Vinh- (bản đẹp) PDFNhung Kim100% (1)
- Unit 1 - Friends Global (HS)Document21 pagesUnit 1 - Friends Global (HS)phúc lao100% (1)
- G11-U4-Bt Bổ TrợDocument22 pagesG11-U4-Bt Bổ TrợBạc Hà SữaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4. Caring For Those in Need: Part 1: Vocabulary and Grammar Review A. VocabularyDocument12 pagesUnit 4. Caring For Those in Need: Part 1: Vocabulary and Grammar Review A. VocabularyCẩm Ly NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 13.unit4 (SM)Document9 pages13.unit4 (SM)Phương Đặng ThảoNo ratings yet
- Revision Unit 4 - (22.11)Document7 pagesRevision Unit 4 - (22.11)thuNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Grade 11guiDocument3 pagesUnit 4 Grade 11gui26- Lê Kiều ThưNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - For A Better CommunityDocument6 pagesTopic 4 - For A Better CommunityOanh PhươngNo ratings yet
- NH Màn Hình 2023-11-19 Lúc 09.34.22Document11 pagesNH Màn Hình 2023-11-19 Lúc 09.34.22myht.c2tc1822.a10No ratings yet
- Review Unit 4-5-6Document19 pagesReview Unit 4-5-6Nguyễn LyNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Thuc Hanh Tieng Anh 9Document188 pagesBai Tap Thuc Hanh Tieng Anh 9Khoa PhạmNo ratings yet
- Unit 10: Communication G8.1 A-VocabularyDocument8 pagesUnit 10: Communication G8.1 A-VocabularyNguyễn Phương ThảoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Practice Test No.1 (24 Ban)Document6 pagesUnit 3 - Practice Test No.1 (24 Ban)nguyen ngaNo ratings yet
- REVISION FOR MID Test Grade 10 2022 2023Document8 pagesREVISION FOR MID Test Grade 10 2022 2023Văn Tài NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Bài tập Tiếng Anh 8 (Bùi Văn Vinh - Chủ biên)Document189 pagesBài tập Tiếng Anh 8 (Bùi Văn Vinh - Chủ biên)AdamNo ratings yet
- Bài tập Tiếng Anh 8 Bùi Văn Vinh Chủ biênDocument186 pagesBài tập Tiếng Anh 8 Bùi Văn Vinh Chủ biênQuỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- UNit 1 No3 Grade 9Document8 pagesUNit 1 No3 Grade 9Thị Huyền Trang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Tiếng Anh Lớp 8 Bùi Văn VinhDocument186 pagesBài Tập Tiếng Anh Lớp 8 Bùi Văn VinhPhương Thu Vũ Thị80% (5)
- UNIT 4 ReviewDocument9 pagesUNIT 4 ReviewHong Phuc Le NguyenNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document8 pagesUnit 4Cô LýNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 World PopulationDocument18 pagesUnit 7 World PopulationkduynNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument191 pagesUntitledMyy HilaryNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 - HSDocument24 pagesUnit 8 - HStruc linhNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document3 pagesUnit 4Mai PhạmNo ratings yet
- Chữa Đề Cương Việt Ba 4-12Document19 pagesChữa Đề Cương Việt Ba 4-12Thanh HươngNo ratings yet
- BÀI TẬP TIẾNG ANH 9- HKIDocument86 pagesBÀI TẬP TIẾNG ANH 9- HKIEllie NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Word FormDocument8 pagesWord FormOanh PhanNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 - HOÀNG THỊ XUÂN HOA - PRINTDocument6 pagesUNIT 4 - HOÀNG THỊ XUÂN HOA - PRINTThanh le phuongNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Grade 11Document17 pagesUnit 3 Grade 11Thảo Quyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 12A6 - Word Form-VocabDocument8 pages12A6 - Word Form-VocabNguyen Thi Phuong ThaoNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Vocab HK1 Unit 3Document9 pagesGrade 7 Vocab HK1 Unit 3Phương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- (BT TẾT) ANH 7Document7 pages(BT TẾT) ANH 7Trân Lưu HuệNo ratings yet
- I. Wordlist: (With IPA)Document22 pagesI. Wordlist: (With IPA)Lâm TùngNo ratings yet
- bài tập unit 1Document12 pagesbài tập unit 1Mai ThiNo ratings yet
- DE CUONG K10 HK 2 2022-2023 - Global SuccessDocument44 pagesDE CUONG K10 HK 2 2022-2023 - Global SuccessNguyen tienNo ratings yet
- Tieng Anh Lop 10 - Unit 3 Music 414df9e368 2Document9 pagesTieng Anh Lop 10 - Unit 3 Music 414df9e368 2Ngân NgânnNo ratings yet
- ĐÁP ÁN - ĐỀ CƯƠNG ÔN TẬP KIỂM TRA CUỐI HỌC KÌ 1Document10 pagesĐÁP ÁN - ĐỀ CƯƠNG ÔN TẬP KIỂM TRA CUỐI HỌC KÌ 1parkjini75No ratings yet
- De Cuong Ontap HK1 (23+24) K10 (ToanVanAnh)Document23 pagesDe Cuong Ontap HK1 (23+24) K10 (ToanVanAnh)chibui089No ratings yet
- Unit 9 (HS)Document10 pagesUnit 9 (HS)huongtradiuhientai5No ratings yet
- SPEAKING-GUIDE-4-5-15.6-HS 2021 OctoberDocument51 pagesSPEAKING-GUIDE-4-5-15.6-HS 2021 OctoberWork RelatedNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Bổ Trợ Tiếng Anh 10 Smart World Học Kì 1 UNIT 1- FAMILY LIFEDocument7 pagesBài Tập Bổ Trợ Tiếng Anh 10 Smart World Học Kì 1 UNIT 1- FAMILY LIFEThuy Nguyen0% (1)
- đề 21-24 Đ.A ĐỀ THI THỬ TUYỂN SINHDocument23 pagesđề 21-24 Đ.A ĐỀ THI THỬ TUYỂN SINHchan phanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document18 pagesUnit 3Van NguyenNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Unit 5 ILLITERACY Co Dap AnDocument48 pagesBai Tap Unit 5 ILLITERACY Co Dap AnTrịnh QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- New Practice 12.1.1Document11 pagesNew Practice 12.1.1linh phương linh50% (2)
- 61. Bài Tập Unit 4 - BVVDocument12 pages61. Bài Tập Unit 4 - BVVnam0385832206No ratings yet
- Bài tập Tiếng Anh 8Document190 pagesBài tập Tiếng Anh 8Thu SangNo ratings yet
- TRỌNG TÂM KIẾN THỨC KĨ NĂNG TA10-MỚIDocument167 pagesTRỌNG TÂM KIẾN THỨC KĨ NĂNG TA10-MỚINguyen Viet LovesUlis80% (5)
- Unit 1 Practice Test 1Document5 pagesUnit 1 Practice Test 1ttnhungNo ratings yet
- E8 Unit 10Document24 pagesE8 Unit 10MsVy English TeacherNo ratings yet
- KEY BT TẾTDocument11 pagesKEY BT TẾTTrân Lưu HuệNo ratings yet
- ANH KC 11- ÔN TẬP GIỮA KỲ 2 2223Document10 pagesANH KC 11- ÔN TẬP GIỮA KỲ 2 2223Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- De Cuong On Tap Giua HK2 TIENG ANH 7Document12 pagesDe Cuong On Tap Giua HK2 TIENG ANH 7Anh Nguyễn HảiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 25Document4 pagesLesson 25Khánh UyênNo ratings yet
- Ôn Tập Kì 2 Unit 13 ActivitiesDocument11 pagesÔn Tập Kì 2 Unit 13 ActivitiesTăng Thùy AnhNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Practice Test No.1 (24 Ban)Document6 pagesUnit 3 - Practice Test No.1 (24 Ban)nguyen ngaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Practice Test No.2 - Gram.2 (25 Ban)Document6 pagesUnit 2 - Practice Test No.2 - Gram.2 (25 Ban)nguyen nga0% (1)
- Unit 2 - Practice Test No. 1Document15 pagesUnit 2 - Practice Test No. 1nguyen nga50% (2)