Description
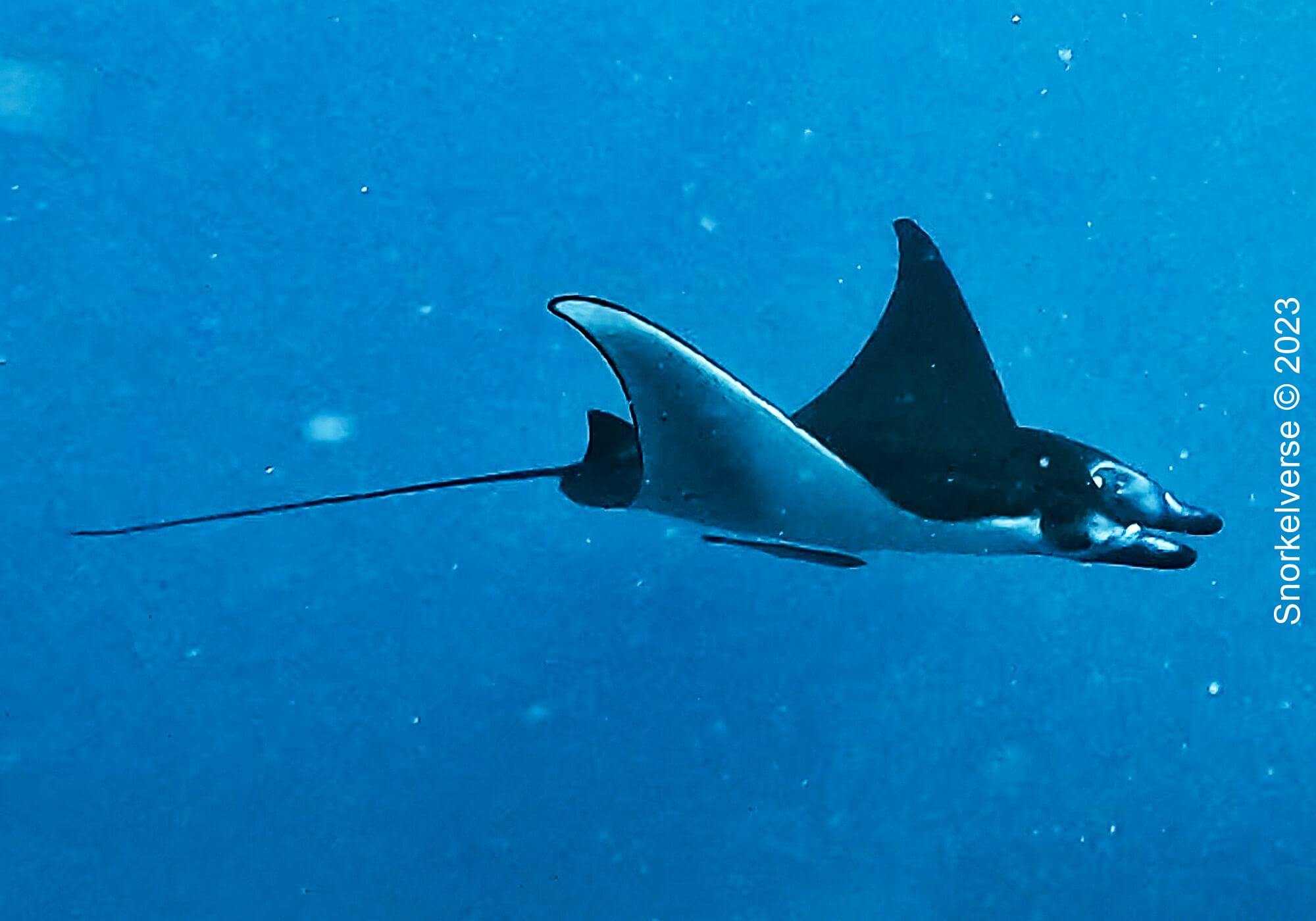
The Reef Manta Ray (Mobula Alfredi) is the second largest type of Ray in the ocean, only smaller to the Atlantic (Giant) Manta Ray. Their wing span can be between 3-3.5 meters, however in some cases can grow beyond 4 meters.
Fact Sheet
Habitat
These majestic fish live in coastal waters of tropical, sub tropical Pacific and Indian oceans. They live in coral reef ecosystems, and open ocean in coastal waters. They like areas with strong currents as the changing water brings in new food.
Diet
These Manta Rays are filter feeders, there diet mainly consists of Plankton, small fish, and micro-organism. They capture their mouth by swimming through the water and passing through their mouth.
Appearance
The Reef Manta Ray is the second largest Manta Ray, and has a wingspan which can reach up to 3.4 meters. They have a dark upper-side and lighter underside, with noticeable black spots. Finally, these Rays have a thin tail that that trails behind them. The tail ranges from 0.5-1 metres in length and isn’t venomous.
Key Features
- Large wings glide through the water majestically
- Two Gill Plates under their mouths
- Green Turtles can often have algae and
Threats
IUCN Conservation Status: Vulnerable
Ship Strikes
Manta Ray’s can be struck by boats, especially in busy areas, such as tourist hot spots. This can lead to injury and fatality.
Climate Change
Climate change affects ocean temperatures, ocean acidity, which directly impacts plankton levels, which the Manta Ray feeds on.
Overfishing
Overfishing in coastal waters can catch the Rays as by-catch, meaning they are caught unintentionally.
Loss Of Habitat
The loss of Coral Reef Ecosystems have a direct impact on these Rays as they rely on the small fish for cleaning and the plankton and small fish to feed on.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where do Reef Manta Ray live?
The Feather Duster Worm is found burrowed into coral and rocks in coral reefs and rocky marine ecosystems, in the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans.
What do Reef Manta Ray eat?
The Feather Duster Worm is found burrowed into coral and rocks in coral reefs and rocky marine ecosystems, in the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans.
What eats Reef Manta Ray?
The Worm has predators including larger fish, such as Triggerfish, and Wrasse. Other predators include Crabs and Crustaceans, Nudibranches (Sea Slugs), and even certain species of Sea Stars and Sea Urchins.
Reef Manta Ray Spotted