What is a Case Citation?
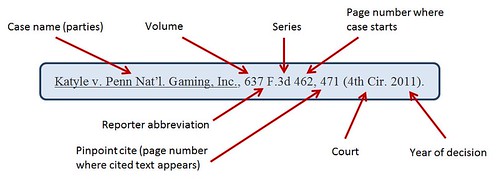
Federal Cases - Examples
B10 (page 11) & Rule 10 (page 95)
U.S. Supreme Court
- Table T1 says to use the official reporter, United States Reports (U.S.) when citing U.S. Supreme Court cases:
- Miranda v. Arizona, 384 U.S. 436 (1966).
- Unofficial reporters
- West's Supreme Court Reporter (S. Ct.)
- Lawyer's Edition (L. Ed.)
U.S. Courts of Appeals
- Table T1 says to use the Federal Reporter (F., F.2d, F.3d) when citing U. S. Courts of Appeals cases:
- Envtl. Def. Fund v. EPA, 465 F.2d 528 (D.C. Cir. 1972).
U.S. District Courts
- Table T1 says to use the Federal Supplement (F. Supp., F. Supp. 2d) when citing U.S. District Court Cases:
- Glover v. Oppleman, 178 F. Supp. 2d 622 (W.D.Va. 2001).
For additional examples, see the Basic Bluebooking--Case Law in Legal Documents tipsheet, provided courtesy of the Law Library at the Pace Law School.
Virginia Cases - Examples
B10 (page 11) & Rule 10 (page 95)
Supreme Court of Virginia (previously Supreme Court of Appeals)
- Official reporter
- Virginia Reports (Va.). See Virginia entry on Table T1 of the Bluebook when citing reporters for cases from 1880 and earlier.
- Unofficial reporters
- Table T1 says to use the South Eastern Reporter (S.E., S.E.2d) when citing to Supreme Court cases:
- Nolte v. MT Tech. Enters., LLC, 726 S.E.2d 339 (Va. 2012)
- Table T1 says to use the South Eastern Reporter (S.E., S.E.2d) when citing to Supreme Court cases:
Court of Appeals
- Official reporter
- Virginia Court of Appeals Reports (Va. Ct. App.)
- Unofficial reporter
- Table T1 says to use the South Eastern Reporter (S.E.2d) when citing to Court of Appeals cases:
- Sapp v. Commonwealth, 546 S.E.2d 245 (Va. Ct. App. 2001).
- Table T1 says to use the South Eastern Reporter (S.E.2d) when citing to Court of Appeals cases:
Circuit Courts
- Official reporter
- Virginia Circuit Court Opinions (Va. Cir. Ct.)
- Ticonderoga Farms, Inc. v. Bd. of Supervisors of Loudon Cnty., 72 Va. Cir. 365 (2006).
- Virginia Circuit Court Opinions (Va. Cir. Ct.)
For additional examples, see the Basic Bluebooking--Case Law in Legal Documents tipsheet, provided courtesy of the Law Library at the Pace Law School.
Official v. Unofficial - What is the Difference?
Cases are published electronically and in print in volumes called court reports or case reporters.
- Official reporters are case reporters designated by statute or court rule as the official reporter for a particular jurisdiction
- Unofficial reporters are case reporters that are not designated as the official reporter for the jurisdiction they cover
The text of an opinion should be identical in both the official and unofficial reporter. The difference between official and unofficial reporters is the research aids and annotations (e.g., headnotes) published along with the case.
Which Reporter Should I Use When Citing a Case?
As law students, follow the Bluebook rules along with any specific guidance from your professor.
For each state, Table T1 (page 227) lists the case reporter you should cite along with its correct abbreviation.
Cases are often published in more than one case reporter. When a case citation includes cites to the same case published in multiple reporters, that is known as a parallel citation. Bluebook Rule 10.3.1(a) (page 103) requires that if a document is being filed in state court, the author must follow local court rules, including rules about whether parallel citations are required.
- If no local rules apply, then Bluebook Rule 10.3.1 applies, which prefers the regional reporter and no parallel citation to the official reporter for most state cases.
Published v. Unpublished - What is the Difference?
Some cases are not designated for publication by the courts.
"Some courts and legislatures have attempted to control the publication of judicial opinions by limiting publication to those opinions that (1) enunciate a new rule of law or change or modify an exisiting rule; (2) apply an established rule of law to a new or significantly different fact situation; (3) involve a legal issue of continuing public interest; (4) criticize existing law; (5) resolve an apparent conflict of authority; or (6) contribute to the legal literature by collecing relevant case law or reciting legislative history." [1]
Unpublished cases can be found in various places:
- West's Federal Appendix is a case reporter that prints the unpublished opinions of the U.S. Courts of Appeals.
- Lexis and Westlaw include unpublished cases in their state and federal case databases.
- Legal newspapers, such as Virginia Lawyers Weekly, selectively publish opinions from unpublished cases.
Use of unpublished cases is governed by court rules. See Rule 10.8.1 (page 112) for information on pending and unreported cases.
__________________________
[1] Steven M. Barkan et al., Fundamentals of Legal Research 35 (9th ed. 2009).
Short Form Citation
Rule B10.2 (page 16) addresses short form citation of case law. Look at the examples listed as part of rule B4 on page 8.
Rule 4 addresses the use of id. and supra.